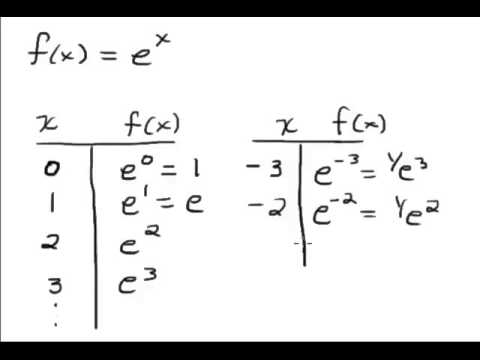
Exponential Graph Yex
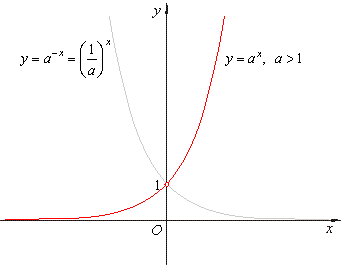
Graphs Of Exponential And Logarithmic Function
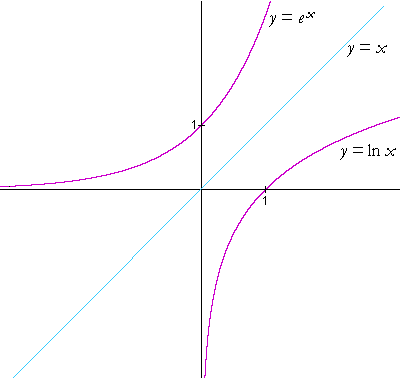
Logarithmic And Exponential Functions Topics In Precalculus

Exponential Functions

12 3 Exponential Functions
Untitled Document
Exponential Functions And Their Graphs
The line clearly does not fit the data.

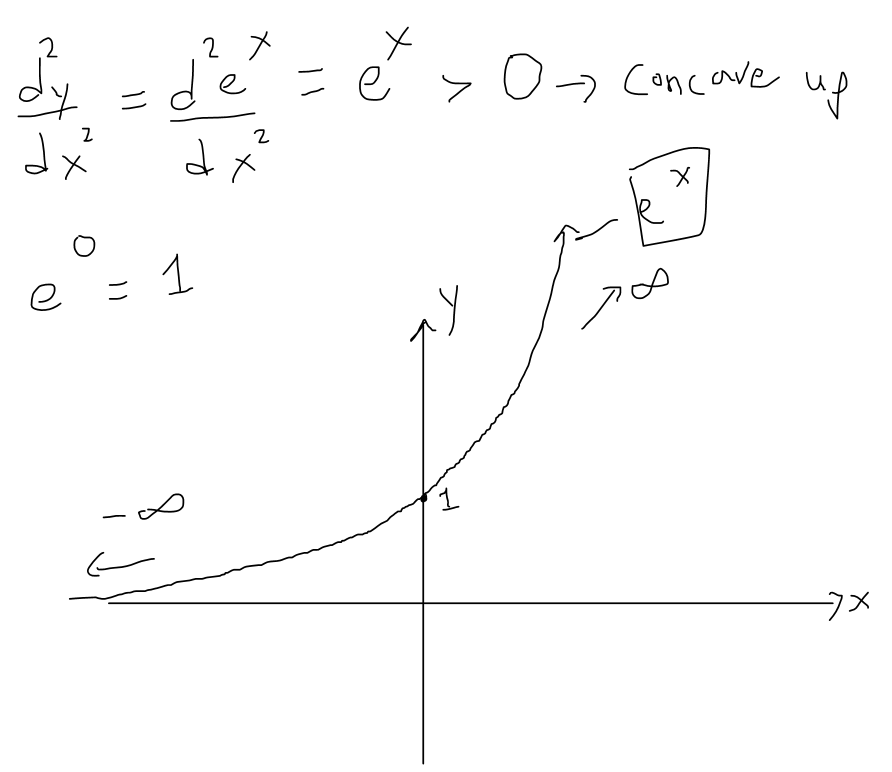
Exponential graph yex. Y = -3 × 0.4 x 3. • d dx ekx = ekx ·k = kekx. The natural log is the logarithm whose base is e.
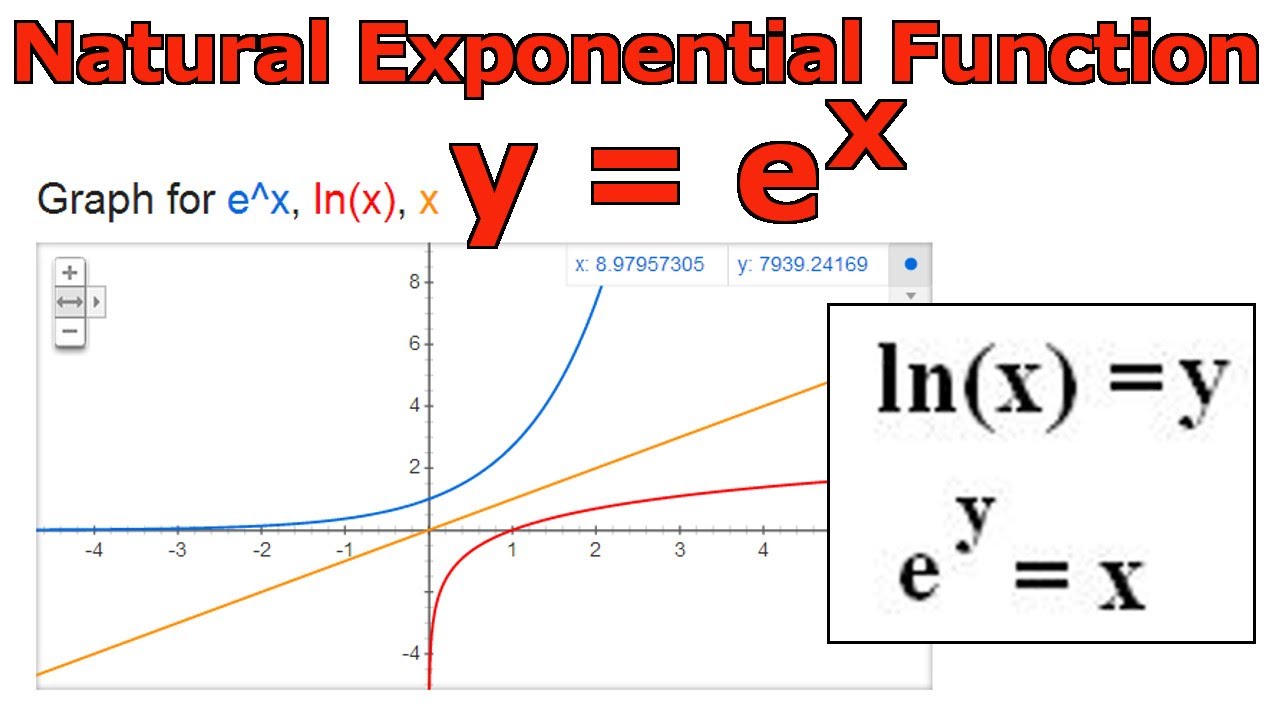
8x = 4 Graphing Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Work with a partner. Pick any point on this function, say (2, ~7.4). The two functions, the natural log and the exponential e, are inverses of each other.
Examples of exponential functions 1. The graph of the natural logarithmic function y = ln x is shown. Y = 0.5 × 2 x 2.
5x = 1 e. For negative x's, the graph decays in smaller and smaller amounts. The logarithm with base e is called the natural logarithm.
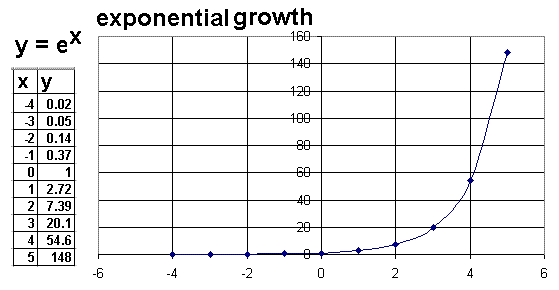
This is called exponential decay. Integrals of Exponential Functions. The data type of Y is the same as that of X.
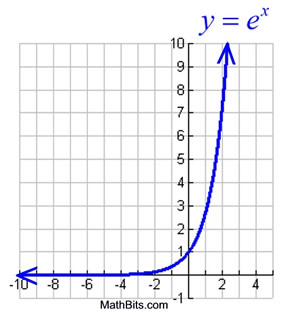
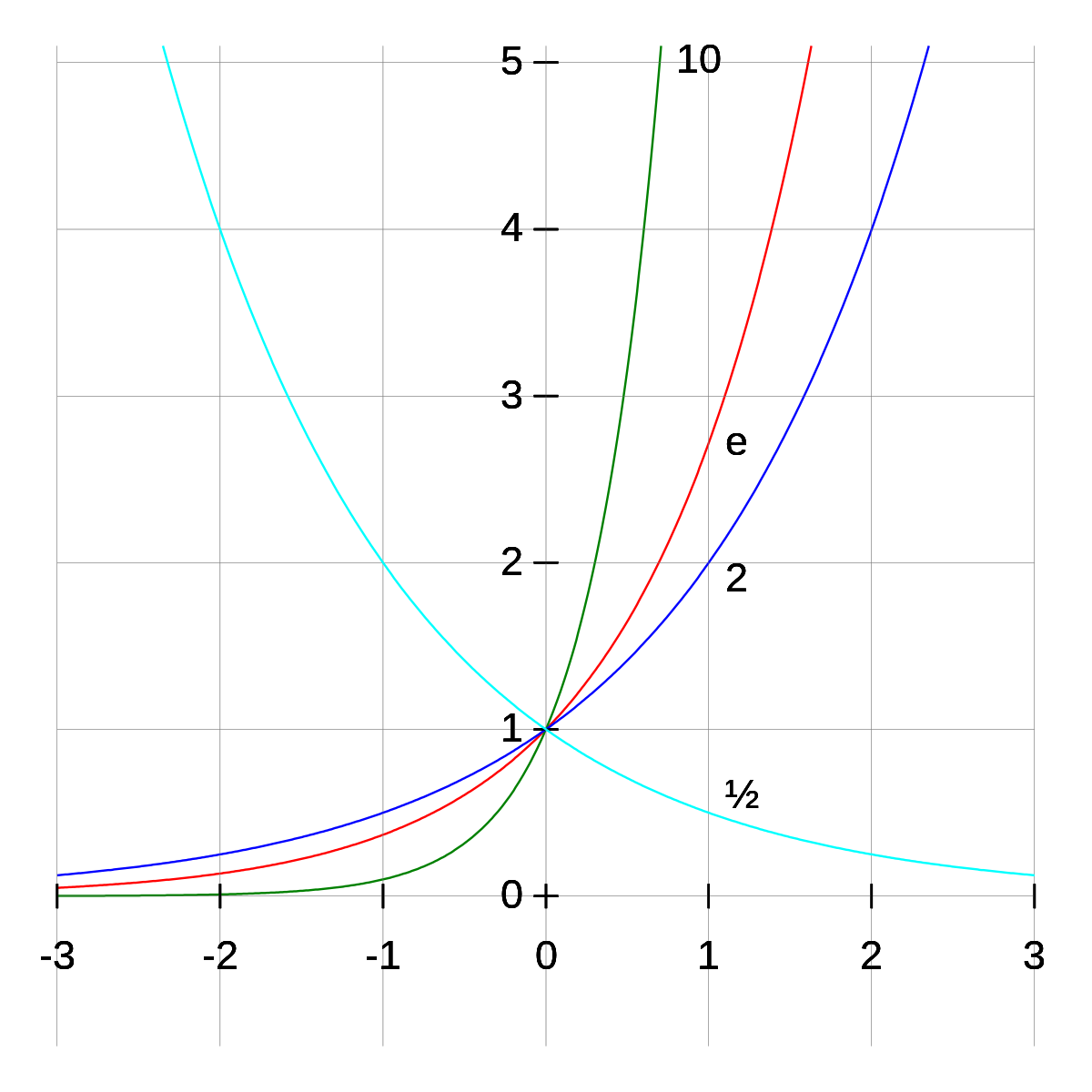
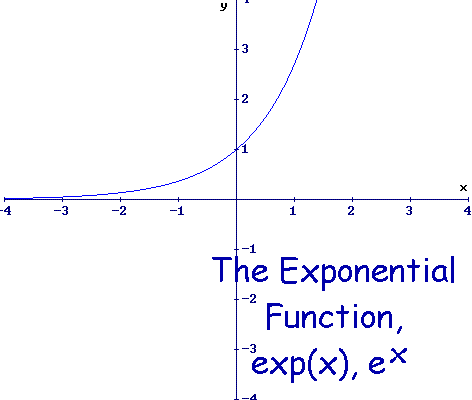
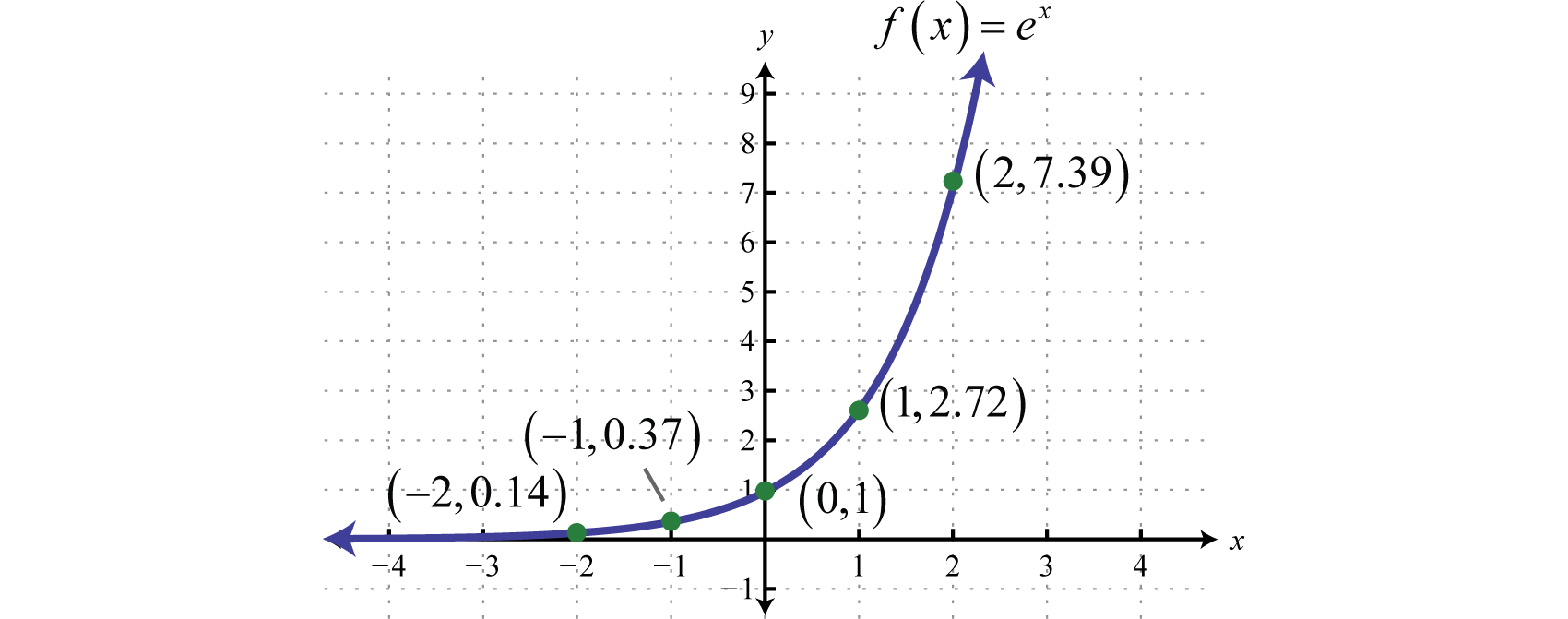
Hence, 10 is called the common base.In fact, the exponential function y = 10 x is so important that you will find a button 10 x dedicated to it on most modern scientific calculators. For real $ x $, the graph of $ y = e ^ {x} $( the exponential curve) passes through the point $ ( 0, 1) $ and tends asymptotically to the $ x $- axis (see Fig.). So, in short, not every exponential equation will be a parabola.
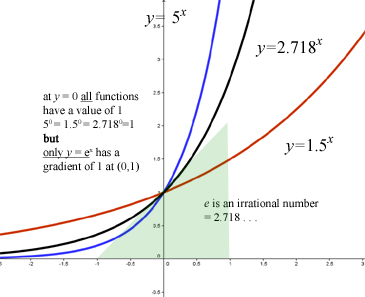
It is special because at any point on the graph the gradient of the curve is equal to the y-value at that point. Label the graphs with their function names. Sketching exponential graphs 2 :.
10.2.1 The Graphs of Exponential Functions Example 10.2 (Exponential Graphs) The graphs of y = f(x) = 3x, y = g(x) = 1.5x, y = h(x) = 0.5x and y = k(x) = 0.2x are drawn below for you. Exponential growth is a specific way that a quantity may increase over time. In a straight line, the “rate of change” is the same across the graph.
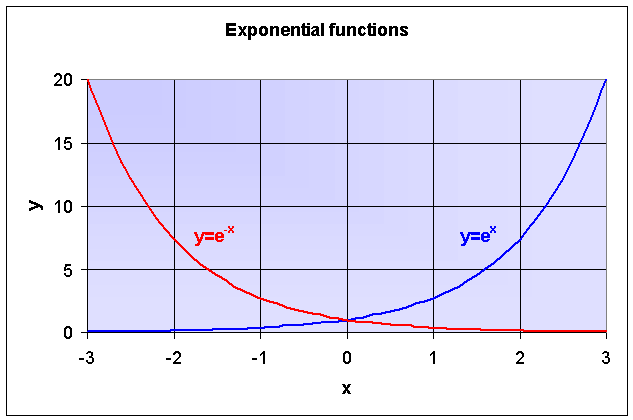
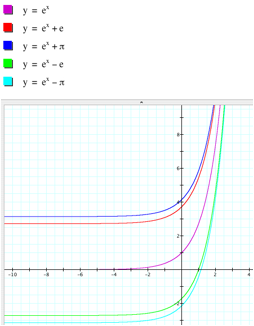
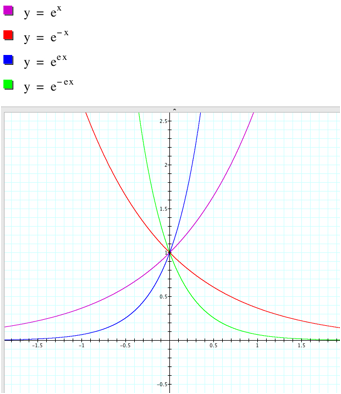
Lastly, let’s observe the effects of parameter c on the graph of the exponential function y = a e bx + c. 5x = 1— 5 f. Graph y=e^ (-x) y = e−x y = e - x Exponential functions have a horizontal asymptote.
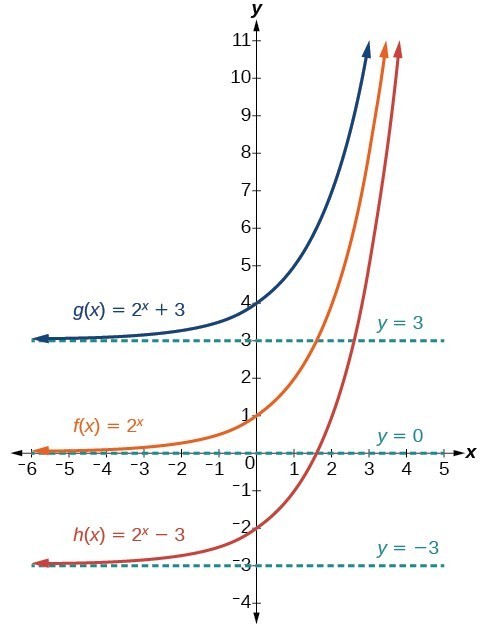
When c > 0 and increases, the graph of y = e x + c is shifted up along the y-axis., and when c < 0 and decreases, the graph of y = e x + c is shifted down along the y-axis. In this section, we explore integration involving exponential and logarithmic functions. Doing so we may obtain the following points:.
Media At this site you can see an example of a base-10 logarithmic scale. Your graphing calculator has a key for ex Graph y ex and then evaluate the following (to 4 dec. Pick two points on the line - (2,4.6) (4,9.2), for example - and determine its slope:.
Transformations of exponential graphs behave similarly to those of other functions. Graph y = e x;. Y = e x 4.
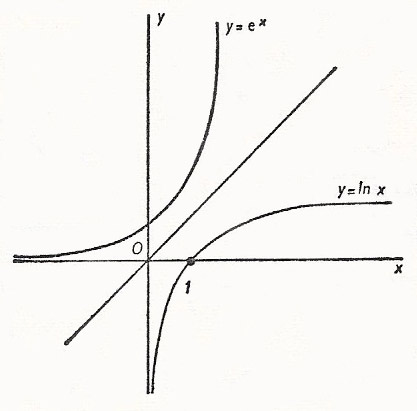
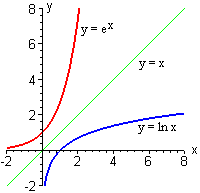
Figure 1.46 The functions y = e x y = e x and y = ln (x) y = ln (x) are inverses of each other, so their graphs are symmetric about the line y = x. Figure 1 The graphs of y = e x and y = in x are reflections of one another about the line y = x, as are all inverse functions. 8x = 4 Graphing Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Work with a partner.
As such, the graphs of these functions are not straight lines. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. The value of e is 2.7181 (to 7 sig.fig.).
The derivative of y=x^2 = 2x (d/dx y=x^2 = 2x). Select to graph the transformed (X, ln(Y) data instead of the raw (X,Y) data and note that the line now fits the data. Areas bounded by exponential functions Figure 8.4 x 1 1 y ex 1 + ex f(x) = _0801.qxd 12/3/04 3:39 PM Page 517.
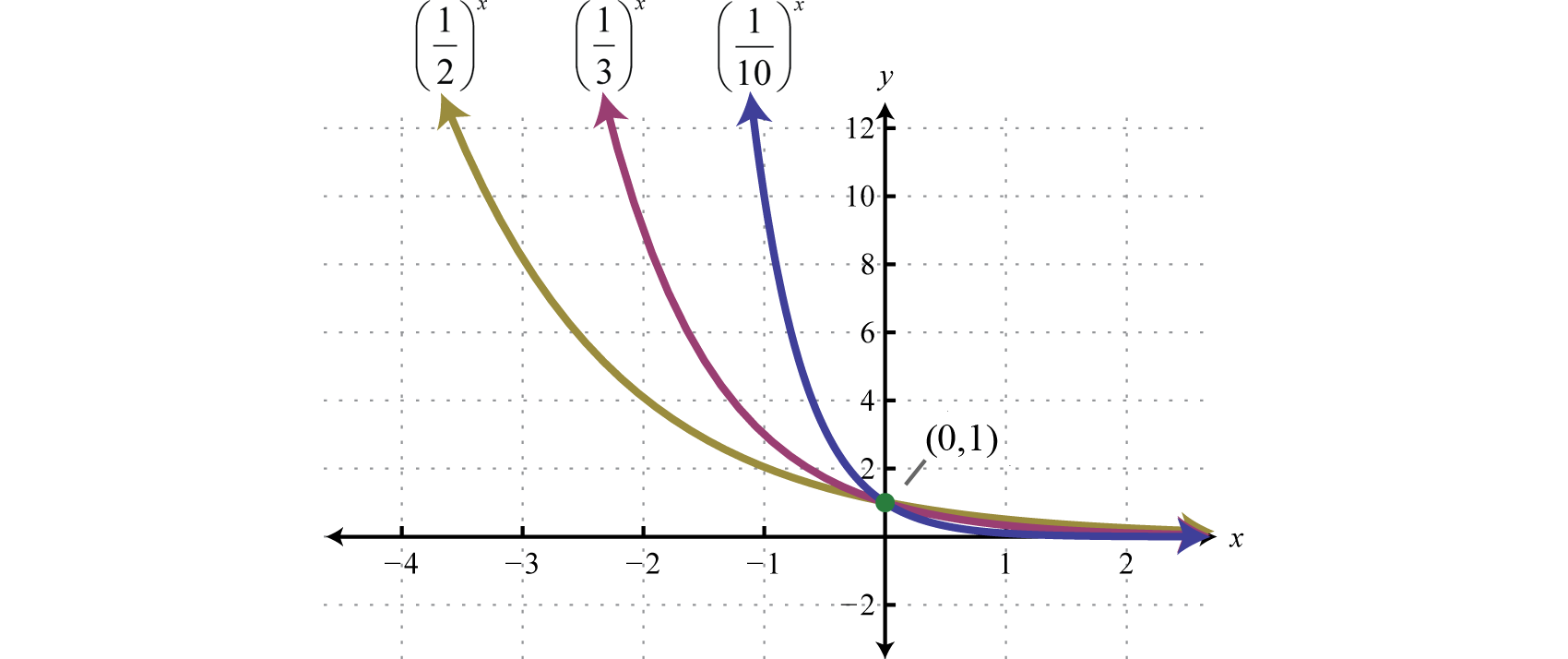
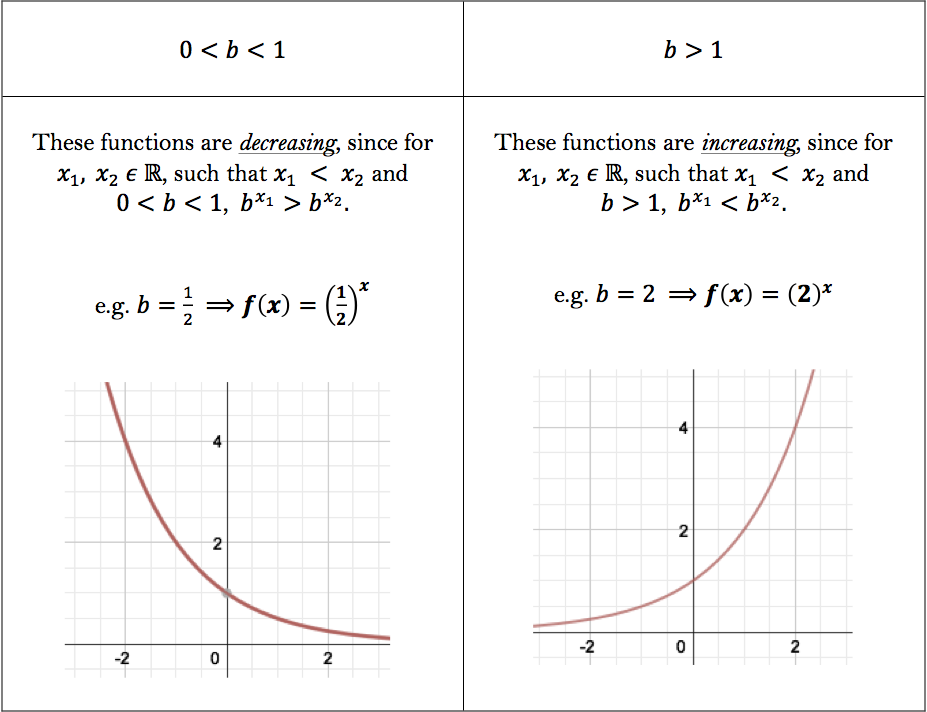
4x = 2 d. If the base of an exponential function is a proper fraction \((0 < b < 1)\), then its graph decreases or decays as it is read from left to right. Y = 10 x Can you tell what b equals to for the.
For instance, it is hard to know where "e. Find the value of x in each exponential equation. Other Formulas for Derivatives of Exponential Functions If u is a function of x , we can obtain the derivative of an expression in the form e u :.
Exponential functions with a base of e are useful for describing continuous growth or decay. Use the graph of y=e x (next card) to sketch the graph y=e x-1 +3. The natural exponential function is the exponential function.
The second graph is just the opposite. Just as with other parent functions, we can apply the four types of transformations—shifts, reflections, stretches, and compressions—to the parent function \(f(x)=b^x\) without loss of shape. Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Let us consider the function latexy=2^x/latex when latexb>1 /latex. Here we sketch the graph of y = e x, and its inverse, y = ln(x). The variable x is an exponent.
3x = 9 c. 5x = 1 e. Exponential Growth and Decay Exponential functions are of the form Notice:.
In Exercises 1 and 2, find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of each function at the point 1. Exponential values, returned as a scalar, vector, matrix, or multidimensional array. 2x = 8 b.
3x = 9 c. It is denoted by ln x. It crosses the y-axis at y = 1, and then decays at slower and slower rates.
I've actually copy and pasted this problem on my little scratch pad so I can mark it up a little bit. The gradient of the graph at the point (1, 2) is 2, etc, etc. Logarithmic functions are the inverse of exponential functions.
Described as a function, a quantity undergoing exponential growth is an exponential function of time, that is, the variable representing time is the exponent (in contrast. The base 10 is used often, most notably with scientific notation. Look at the graph of y = e x in the following figure.
Y a > 0, b > 0, L > 0 L. Derivatives of sin(x), cos(x), tan(x), eˣ & ln(x) Derivative of aˣ (for any positive base a) Practice:. Proof By the chain rule, d dx eu = d du (eu) du dx = eu du dx Examples 8.
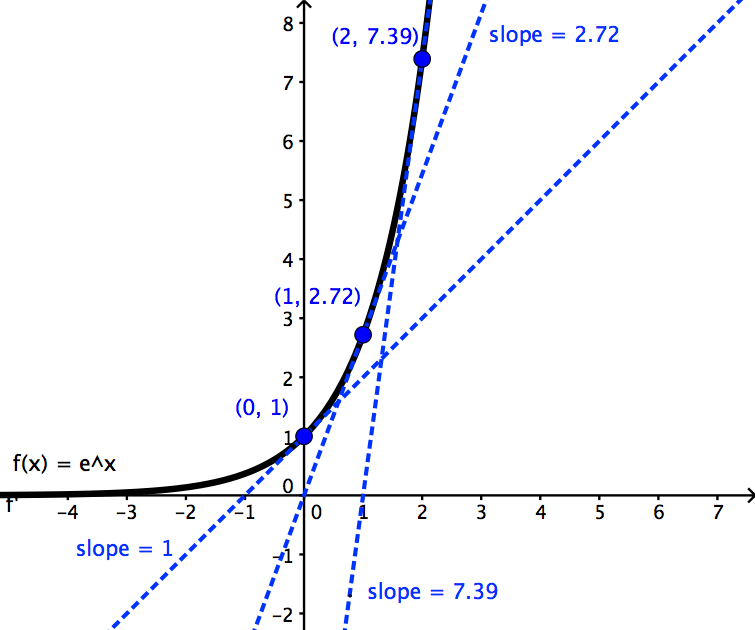
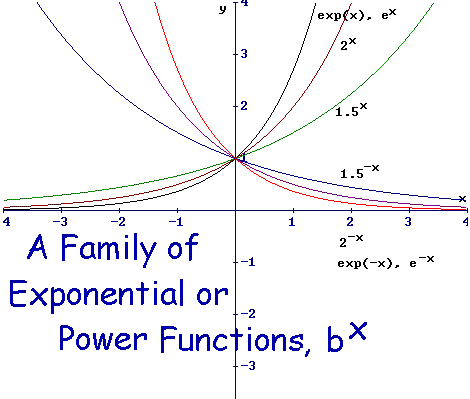
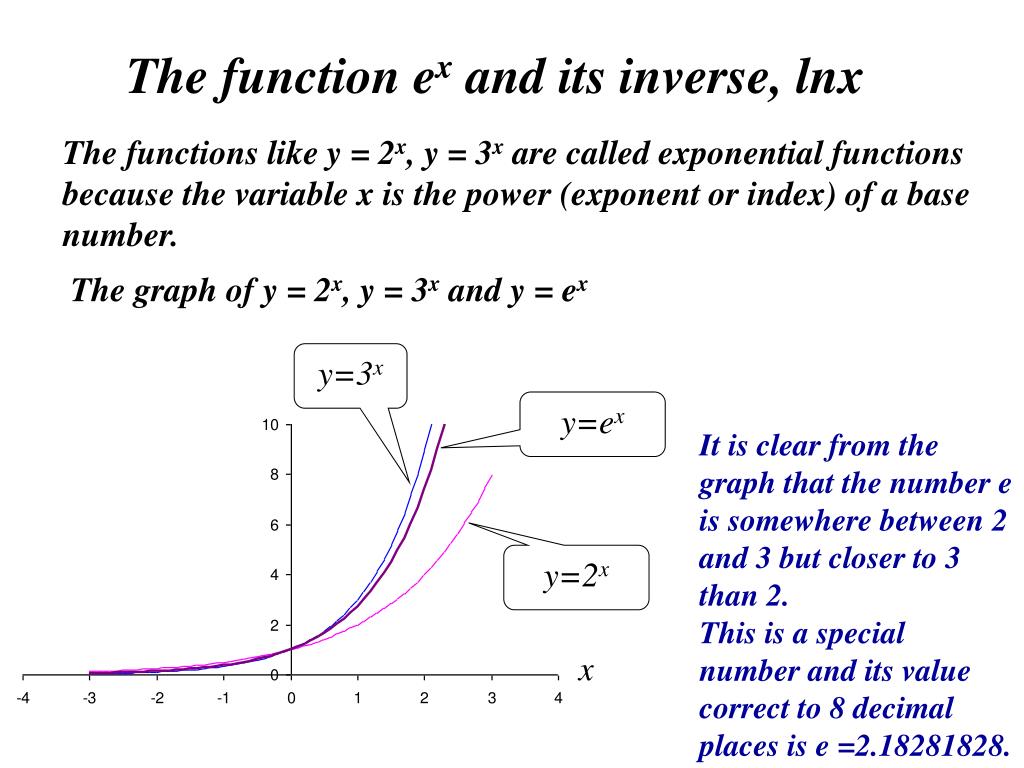
Since 2 < e < 3, the graph of the natural exponential function lies between the graphs of y = 2x and y = 3x, as shown below. Natural Logarithmic Function. The gradient of the graph at the point (0, 1) is 1.
• d dx e √ x = e x · d dx √ x = e x · 1 2 √ x y = e √ x 2 √ x • d dx e−x2 = e−x2 d dx −x2 = e−x2 (−2x. Find the value of x in each exponential equation. First, the property of the exponential function graph when the base is greater than 1.
As you can see from the figure above, the graph of an exponential function can either show a growth or a decay. 5x = 1— 5 f. In this example, we will sketch the basic graph y = 10.
Complete each table for the. Graphing Exponential Functions Graph the function, not by plotting points, but by starting from the graphs of y = e x in Figure 1.State the domain, range, and asymptote. Ea In mathematical analysis one considers the exponential function $ y = a ^ {x} $ for real $ x $ and $ a > 0 $, $ a \neq 1 $;.
It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. (reflections) Show Step-by-step Solutions. Also, y=e^x is not a parabola.
In this tutorial I show you how to transform the basic graph of y=e x using translations to sketch the graphs of. Let us consider the exponential function, y=2 x. The exponential function, y = e x, y = e x, is its own derivative and its own integral.
If the base of an exponential function is greater than \(1 (b > 1)\), then its graph increases or grows as it is read from left to right. Sketching exponential graphs 1 This is the 1st in a series of 3 tutorials where I show you how to sketch exponential graphs which are transformations of y = e x. Graph y = e x 2.
Graphing an exponential function & its inverse (1 of 2) The key to graphing exponential and logarithmic functions is remembering that they're inverses, and have mirror symmetry across the line y = x. 2x = 8 b. It is often referred to as the exponential function.
The natural logarithmic function, y = ln x, is the inverse of the natural base exponential function, y = e x. Chain Rule Lemma 7. It is also the unique positive number a such that the graph of the function y = a x has unit slope at x = 0.
For real values of X in the interval (-Inf, Inf), Y is in the interval (0,Inf).For complex values of X, Y is complex. In general, the graph of the basic exponential function y = a x drops from ∞ to 0 when 0 < a < 1 as x varies from − ∞ to ∞ and rises from 0 to ∞ when a > 1. Y = e x is a special exponential function.
This might feel a bit more difficult to graph, because just about all of my y-values will be decimal approximations.But if I round off to a reasonable number of decimal places (one or two is generally fine for the purposes of graphing), then this graph will be fairly easy. However, the derivative of y=e^x = e^x. The exponential function y = a x , can be shifted k units vertically and h units horizontally with the equation y = a ( x + h ) + k.
If h < 0, the graph would be shifted h units right. Note that the domain of ln x, like all logarithmic functions of form y = log a x, is (0,∞). Note that, for graphing, the decimal approximations are more useful than the "exact" forms.
One way to graph this function is to choose values for latexx/latex and substitute these into the equation to generate values for latexy/latex. The exponential function is perhaps the most efficient function in terms of the operations of calculus. Starting with a color-coded portion of the x y {\displaystyle xy} domain, the following are depictions of the graph as variously projected into two or three dimensions.
F xe= x with base e. Based only on these three points, plot the three corresponding points that must be on the graph of y is equal to log base b of x by clicking on the graph. Parent Graphs of Exponential Functions.
Voiceover:The three points plotted below are on the graph of y is equal to b to the x power. Y = e − x − 1. This function is related to the (basic) exponential function $ y = e ^ {x} $ by.
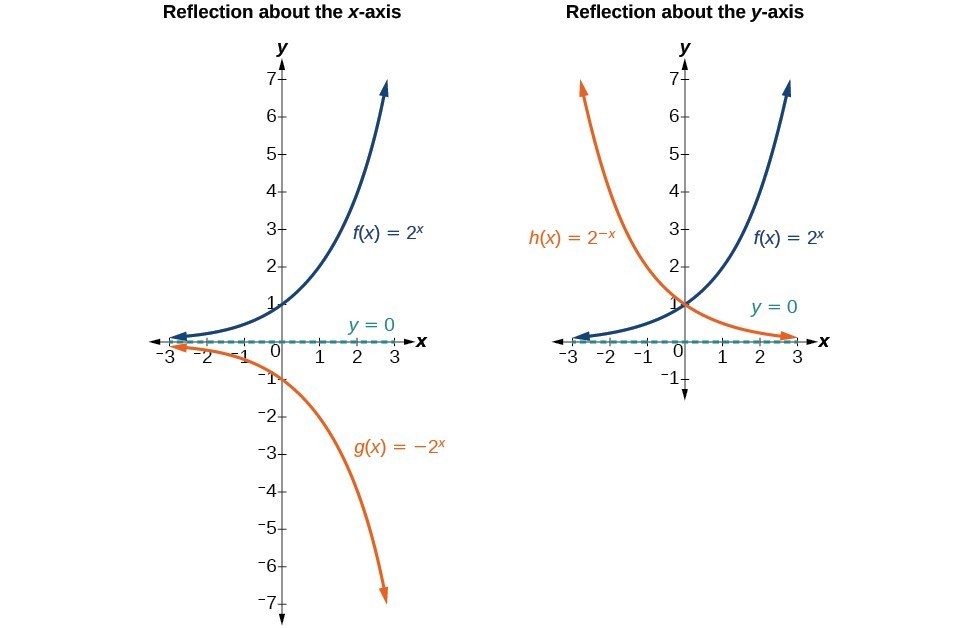
Then use the value of x to rewrite the exponential equation in its equivalent logarithmic form, x = log b y. In addition to shifting, compressing, and stretching a graph, we can also reflect it about the x-axis or the y-axis.When we multiply the parent function latexf\left(x\right)={b}^{x}/latex by –1, we get a reflection about the x-axis.When we multiply the input by –1, we get a reflection about the y-axis.For example, if we begin by graphing the parent function latex. Then use the value of x to rewrite the exponential equation in its equivalent logarithmic form, x = log b y.
Every once in a while they'll give you a more-complicated exponential function to deal with:. You can easily find its equation:. Review your exponential function differentiation skills and use them to solve problems.
Here are some examples of parent exponential graphs. ExamSolutions - youtube Video. In Example #1 the graph of the raw (X,Y) data appears to show an exponential growth pattern.
Although it might appear that the y values of the logarithmic graph “level out,” as if approaching a horizontal asymptote, they do not. Definition image Term image Definition. The graph of the exponential function is a two-dimensional surface curving through four dimensions.
4x = 2 d. We can see that in each case, the slope of the curve `y=e^x` is the same as the function value at that point. The height of the function at that point, ~7.4, is the same as the slope at that point.
The graph of function y=2 x is shown below. Sketching exponential graphs 1 :. Complete each table for the.
Or root feature of a graphing utility.) y e x y L 2. Y = ex - 2 (2 tims to the right) y = ex-2 (2 down) y = e2x (horizontal stretch 1/2. Graphing Transformations of Exponential Functions.
Exponential Function Graph for y=2 x. A) e2 b) e4 c) e 3 NOTE:. The equation of the horizontal asymptote is y = 0 y = 0.
The (natural) exponential function f(x) = e x is the unique function which is equal to its own derivative, with the initial value f(0) = 1 (and hence one may define e as f(1)).The natural logarithm, or logarithm to base e, is the inverse function to the natural exponential function. E is a _____, not a _____. The exponential graph of a function represents the exponential function properties.
If you can’t memorize this rule, hang up your calculator. Graphing an Exponential Function Example 1. I will compute some plot-points, as usual:.
The graph passes through the point (0,1). EXponenTIAL AnD LoGARITHMIc FUncTIonS - LeSSon 6 59 LeSSon 6 eXponenTIAL AnD LoGARITHMIc FUnc-TIonS Exponential functions are of the form y = ax where a is a constant greater than zero and not equal to one and x is a variable. F (x) = 10 x + 5.
Derivatives of aˣ and logₐx. Sketch the graph and determine the domain and range:. 2 Differentiation and Graphing 2.1 Chain Rule Differentiation:.
The figure on the left shows exponential growth while the figure on the right shows exponential decay. In these graphs, the “rate of change” increases or decreases across the graphs. For simplicity, let’s set a = 1, and b = 1.
I always remember that the “reference point” (or “anchor point”) of an exponential function (before any shifting of the graph) is \((0,1)\) (since the “\(e\)” in “exp” looks round like a “ 0 ”). The Natural Exponential Function:. An exponential function is a function that includes exponents, such as the function y=e x.A Graph of an exponential function becomes a curved line that steadily gets steeper, like the one at the right.
Exponential Functions
Search Q Exponential Function Tbm Isch
Q Tbn 3aand9gct4ngiodots Jsgomg T Abhe7hyzncx78gourkta Oyr1tekkd Usqp Cau
Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra

Exponential Function Wikipedia

7 1 The Natural Logarithm Function
What Is The Graph Of E X Quora
Graphing Exponential Functions
Why Is E X A Non Periodic Function Quora
Natural Exponential Function And Natural Logarithmic Function Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math

Transformation Of Graphs By Modulus Function Functions Openstax Cnx
Transforming Exponential Graphs Example 2 Video Khan Academy

Pure Maths Academic Skills Kit Ask Newcastle University

Bestmaths
Derivative Of E X Wyzant Resources
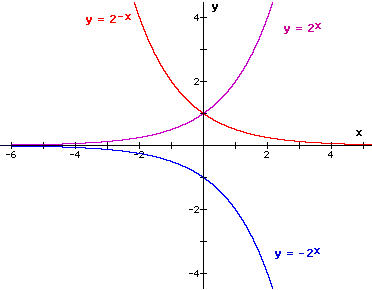
Bestmaths

A Review Of Logarithms
6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function
Use Of Log Log Plane And Semi Log Plane
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq67l V4i1hza30xk01vn2iwplpq1mmvrzhd93f37uco0ekgjhy Usqp Cau
Transforation Of Exponential Graphs Y Ex Matching Cards With Answers Teaching Resources

Exponential Function Wikipedia

Introduction We Are Going To Look At Exponential Functions We Will Learn About A New Special Number In Mathematics We Will See How This Number Can Be Ppt Download

Transformation Of Exponential Functions Examples Summary Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Review

Biomath Exponential Functions

Bestmaths

Biomath Exponential Functions
Exponentiation Wikipedia
Exponential Functions

Functions And Models 1 Exponential Functions Ppt Download
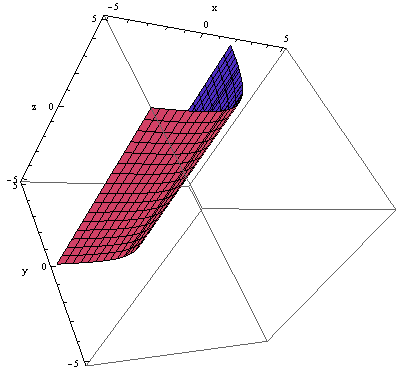
Sketch The Graph Of Y E X As A Surface In R 3 Homework Help And Answers Slader
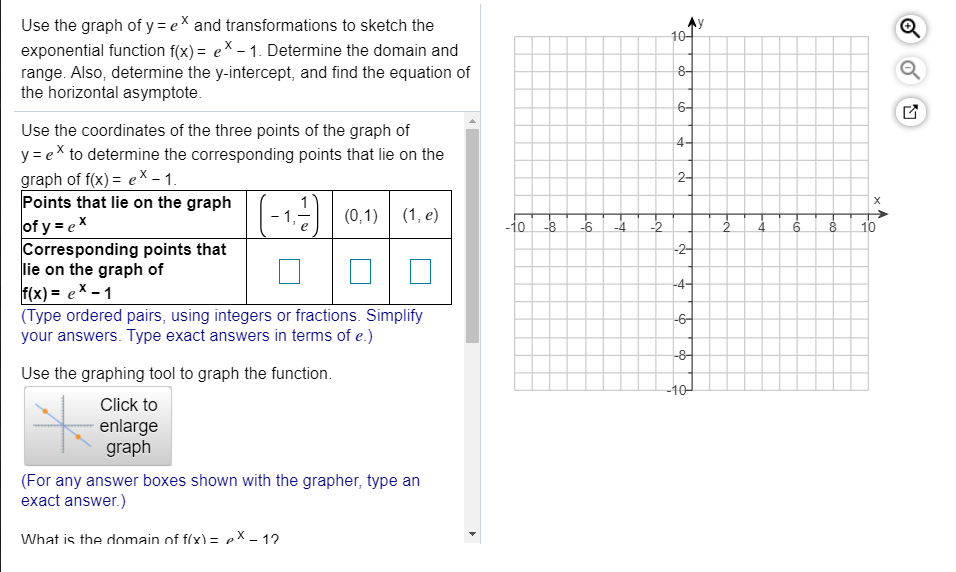
Solved Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Sket Chegg Com

Exponential Function Encyclopedia Of Mathematics
Function And Relation Library
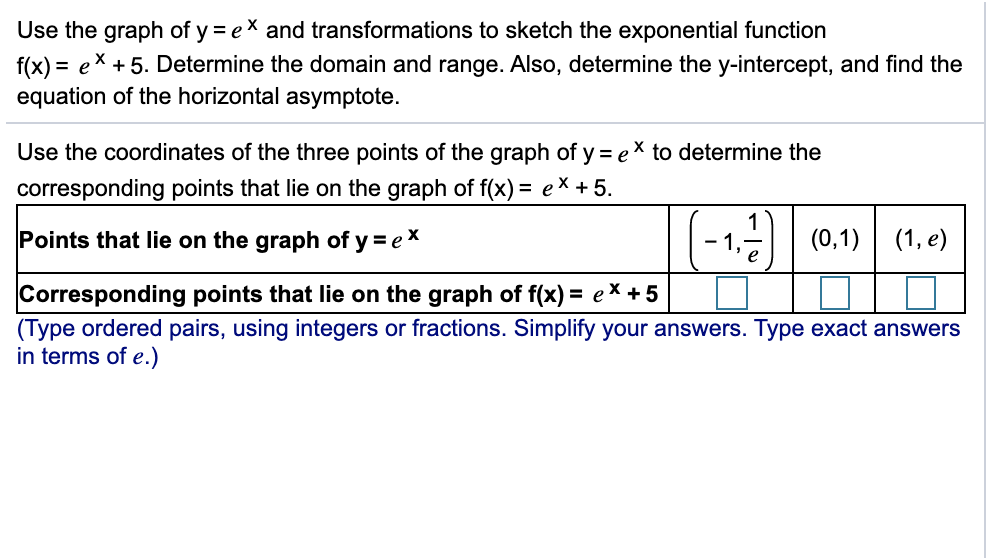
Solved Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Sketc Chegg Com
Solved Part B F X 0 1 X Complete The Table Of Coordin Chegg Com
Function And Relation Library
Derivative Exponentials Natural Logarithms Differential Calculus From A Level Maths Tutor
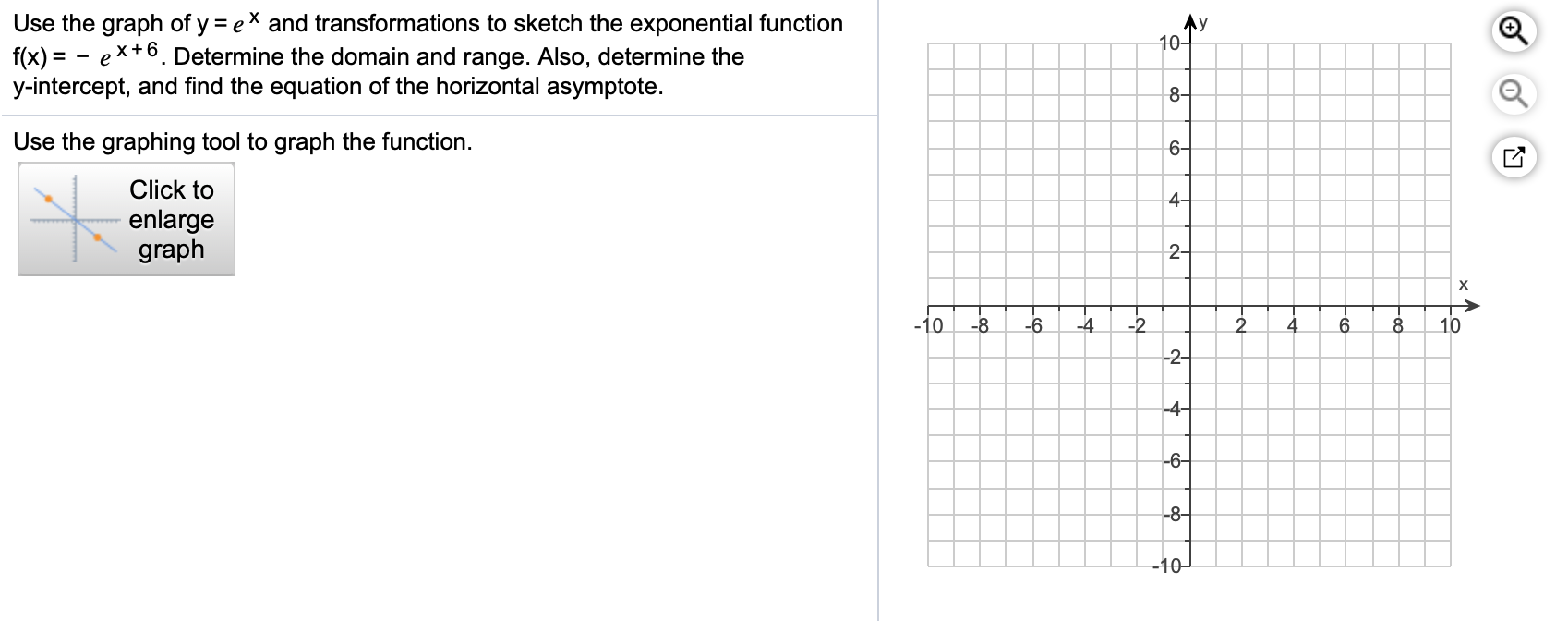
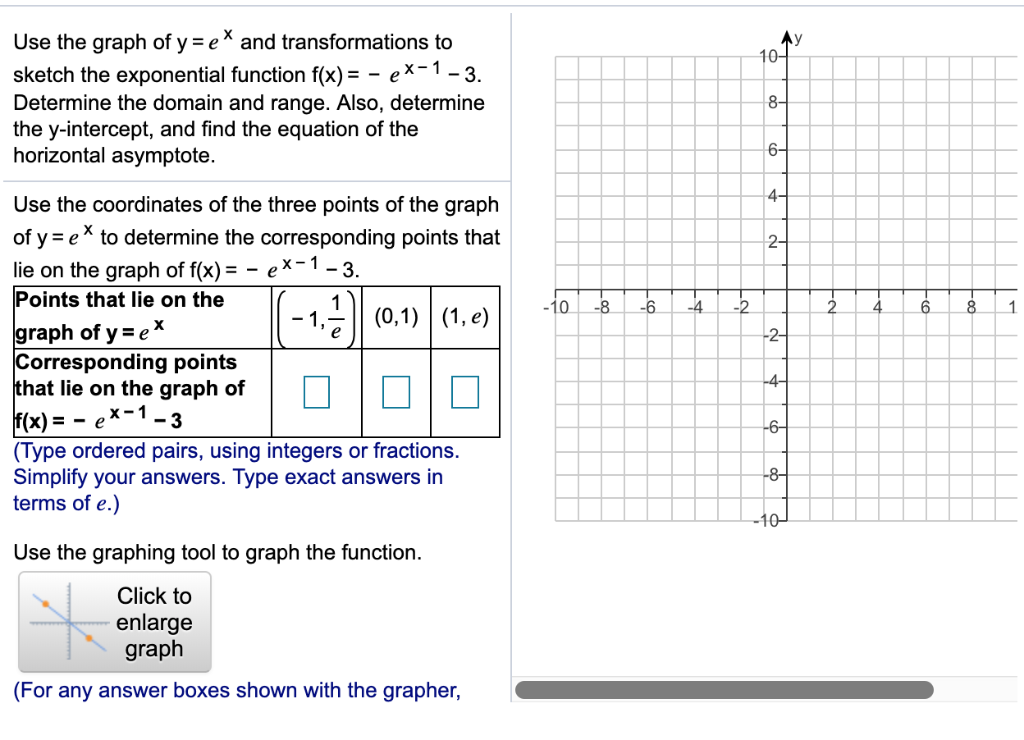
Solved Use The Graph Of Y Ex And Transformations To Ske Chegg Com
Exponential
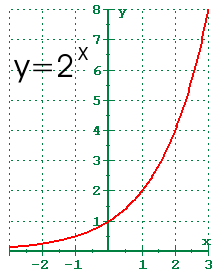
4 1 Exponential Functions And Their Graphs

The Exponential Function Math Insight

The Logarithm And Exponential Functions

The Number E And The Function E X
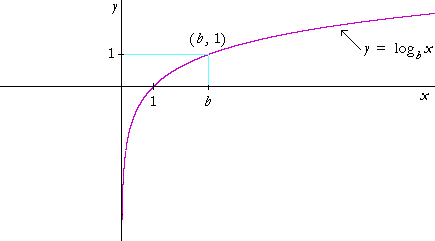
Logarithmic And Exponential Functions Topics In Precalculus
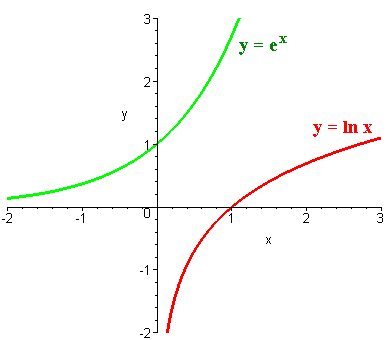
Logarithms
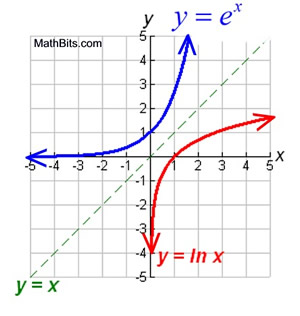
Natural Exponential Function And Natural Logarithmic Function Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math

Review
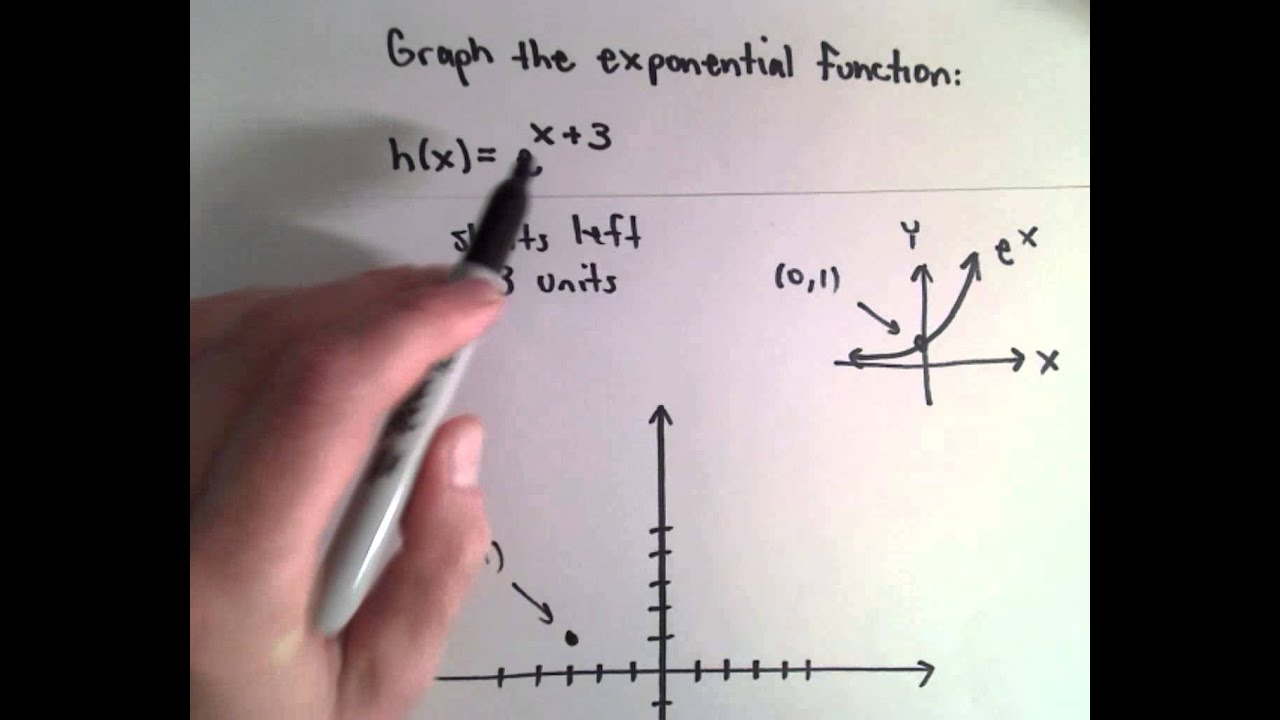
Graph Of Y E X 3 Using Graph Transformations Youtube

The Logarithm And Exponential Functions
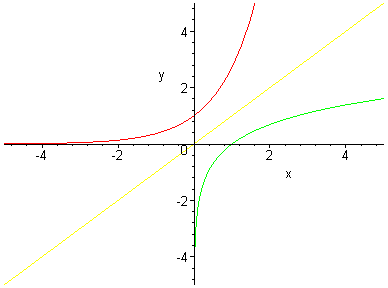
Exponentials And Logarithms Maths A Level Revision
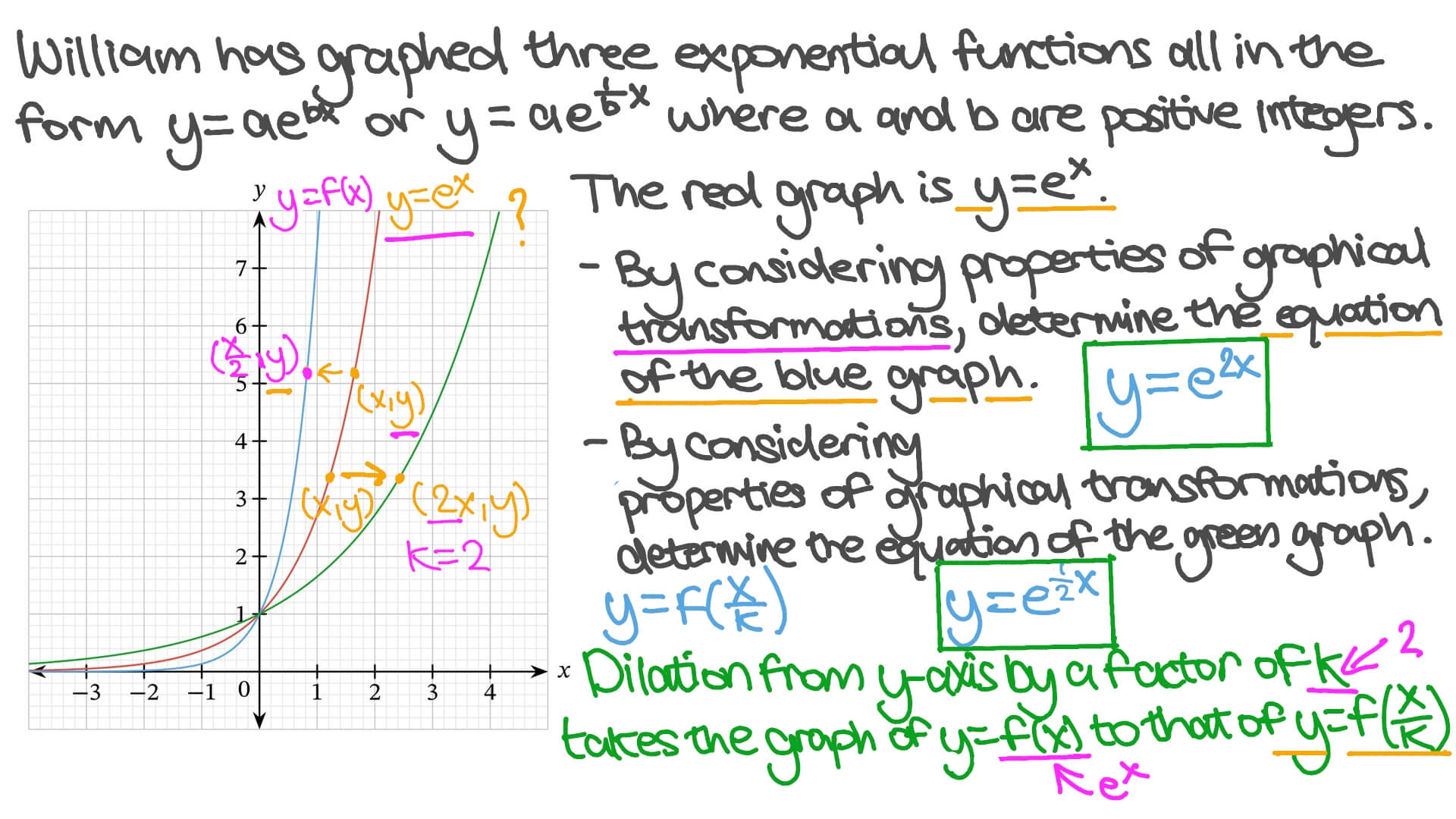
Video Graph Transformations Of Exponential Functions Nagwa
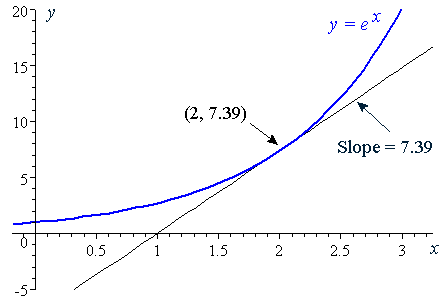
6 Derivative Of The Exponential Function

12 3 Exponential Functions
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrpyzokdjrkkdydro Q92iv8me1eehwkmjb4zrnjr8 Usqp Cau

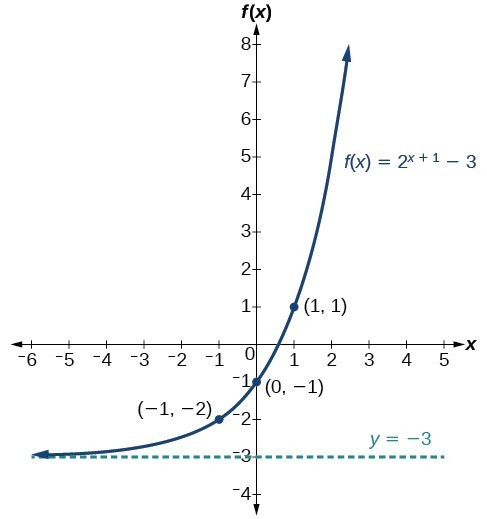
The Graph Of Y E X 3 Is Shown What Are The Y Intercept And The Horizontal Asymptote And Do Brainly Com
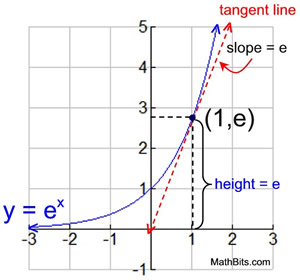
Natural Exponential Function And Natural Logarithmic Function Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math

Exponential Functions Ck 12 Foundation
Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra
Stretching Compressing Or Reflecting An Exponential Function College Algebra
Exploring Exponential Functions
Functions And Their Inverses Worked Examples
Graph Of E X Youtube
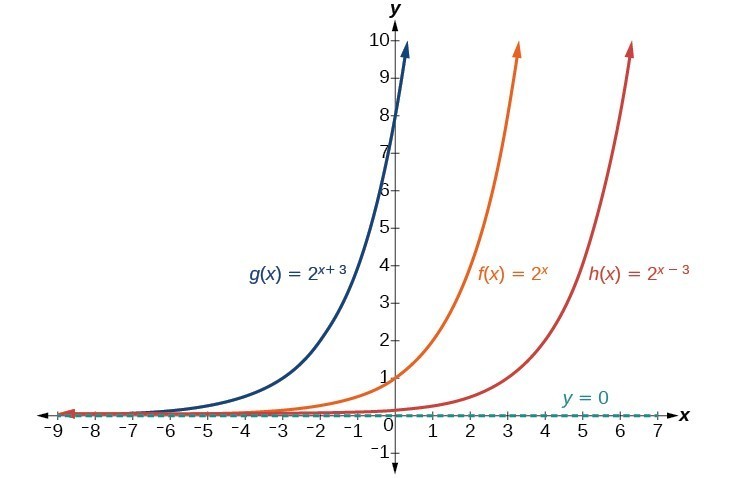
Graph Exponential Functions Using Transformations College Algebra

Working With Exponentials And Logarithms
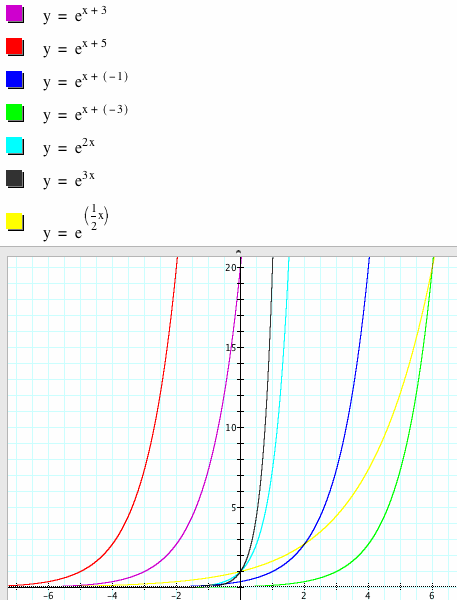
Exploring Exponential Functions
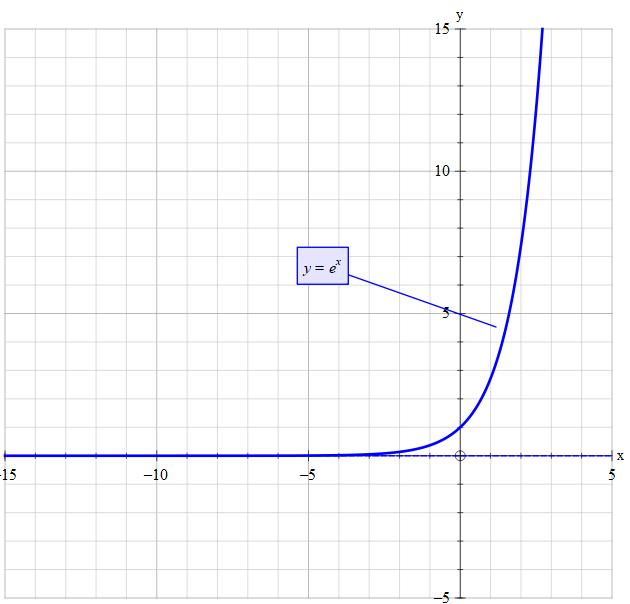
What Is The Domain And Range Of Y E X Socratic

Solved Use The Graph Of Y E And Transformations To Sketc Chegg Com
Inverse Functions Part 1
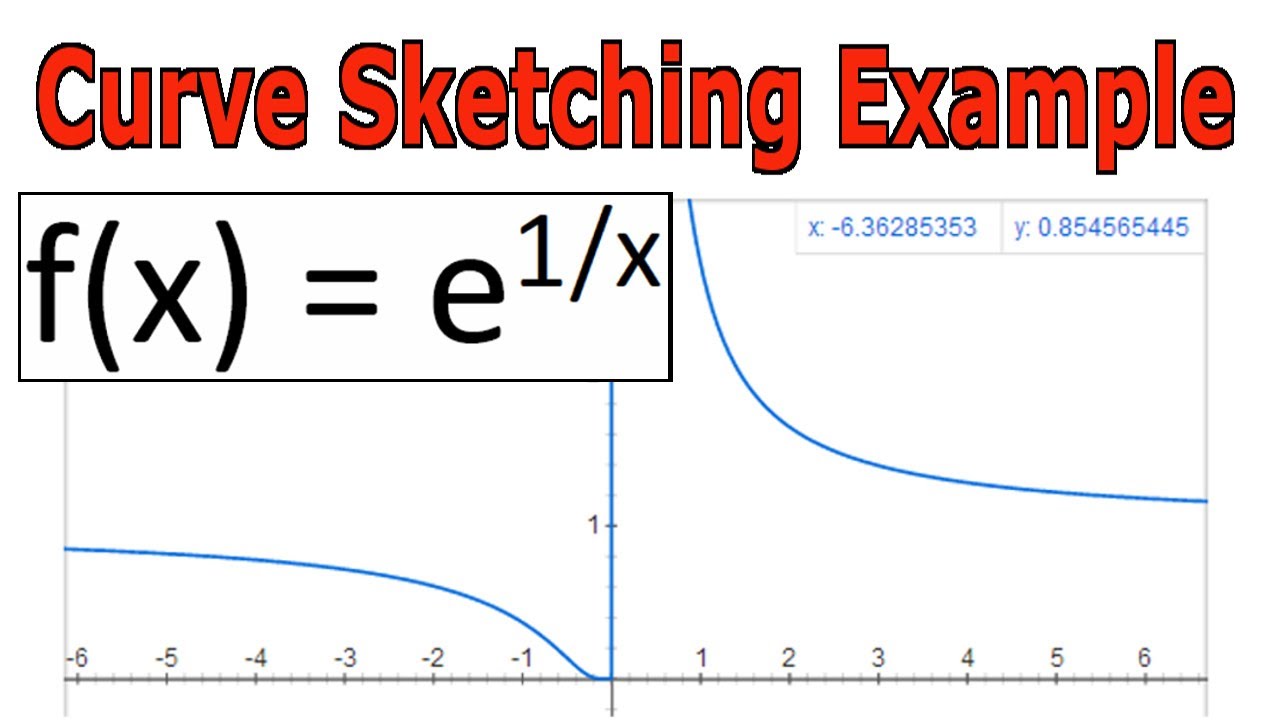
Curve Sketching Example Y E 1 X Youtube

Exponential Function Wikipedia
Amy S Write Up 12
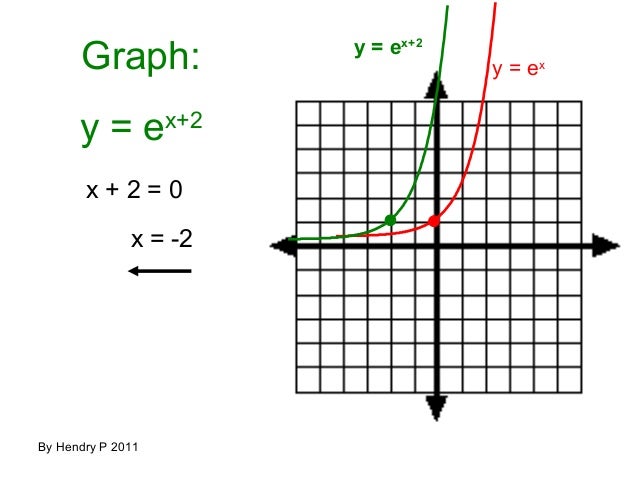
Fungsi Eksponen Dan Logaritma
Graphing The Natural Exponential Function Y E X Peakd

The Logarithm And Exponential Functions
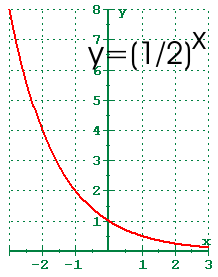
4 1 Exponential Functions And Their Graphs

Transforation Of Exponential Graphs Y Ex Matching Cards With Answers Teaching Resources

Transforming Exponential Graphs Example 2 Video Khan Academy
Natural Exponential Function Y E X Youtube
Ppt The Function E X And Its Inverse Lnx Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

E Mathematical Constant Wikipedia
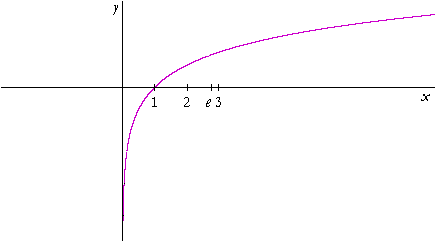
Logarithmic And Exponential Functions Topics In Precalculus
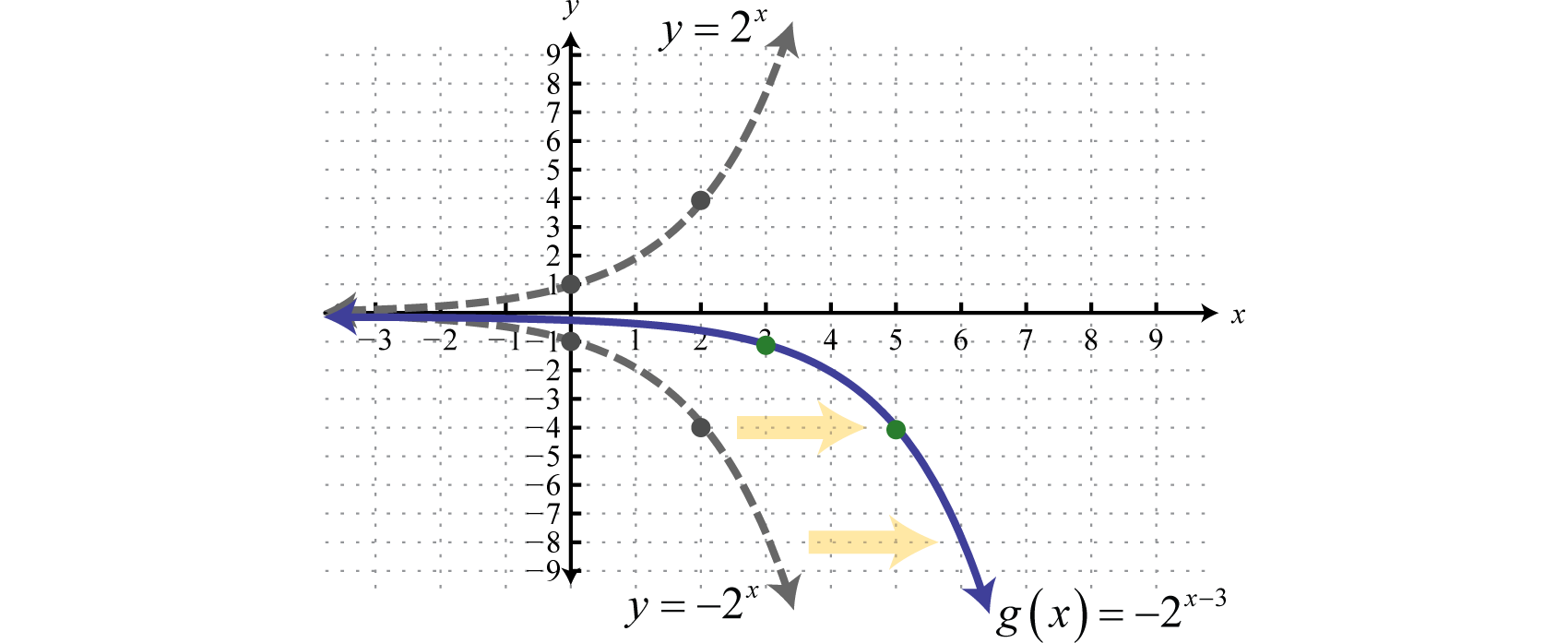
Exponential Functions And Their Graphs

Logarithmic And Exponential Graphs

Transforming Exponential Graphs Video Khan Academy

Jabbamatheez 40s Winter 08 Introduction To Exponential Modeling Ish
Exponential Functions And Their Graphs
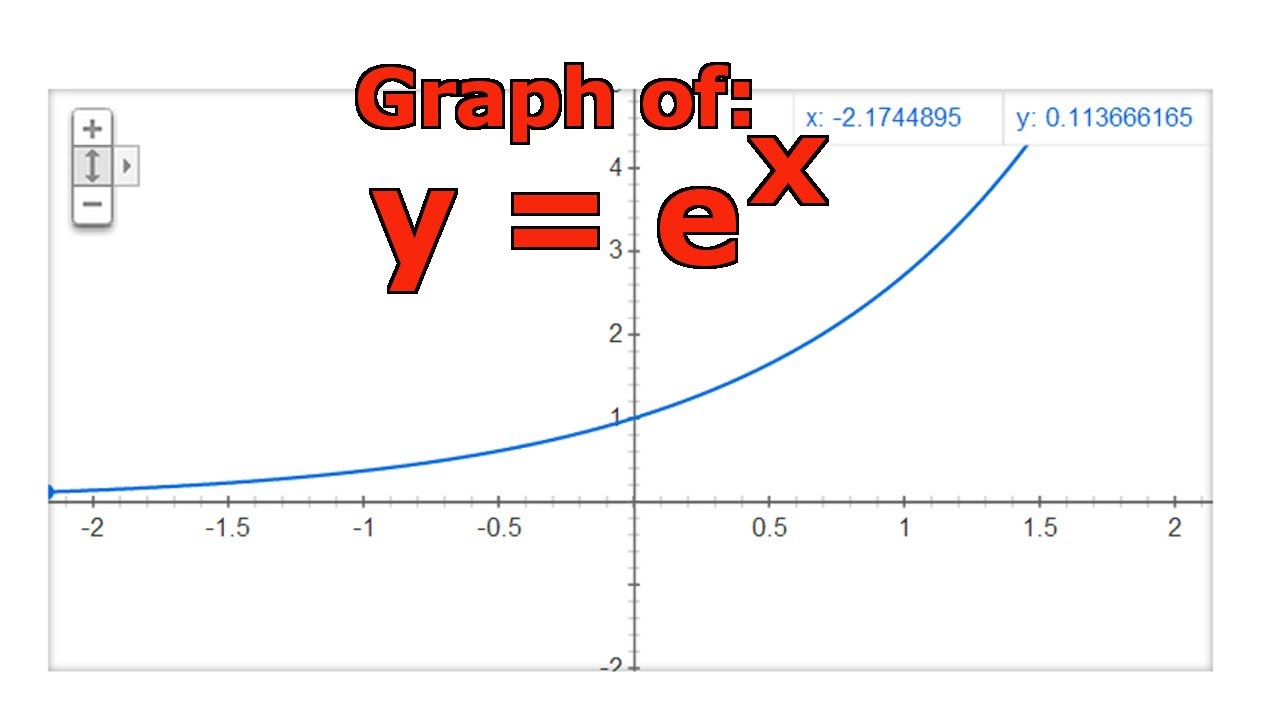
Graphing The Natural Exponential Function Y E X Youtube

Bestmaths
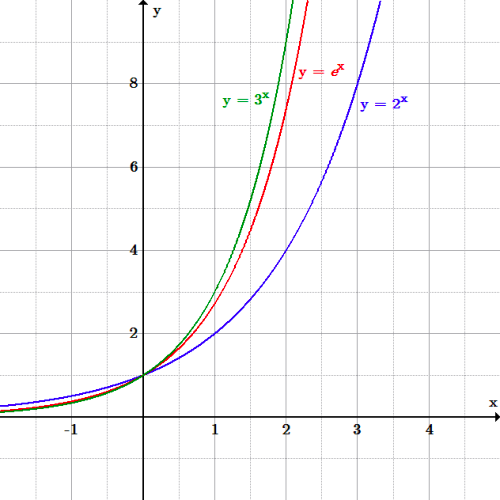
The Real Number E Boundless Algebra
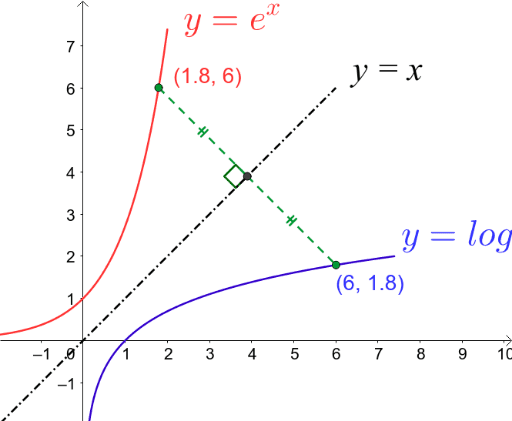
Graphs E X And Ln X Geogebra

Exponetials And Growth Functions

Working With Exponentials And Logarithms
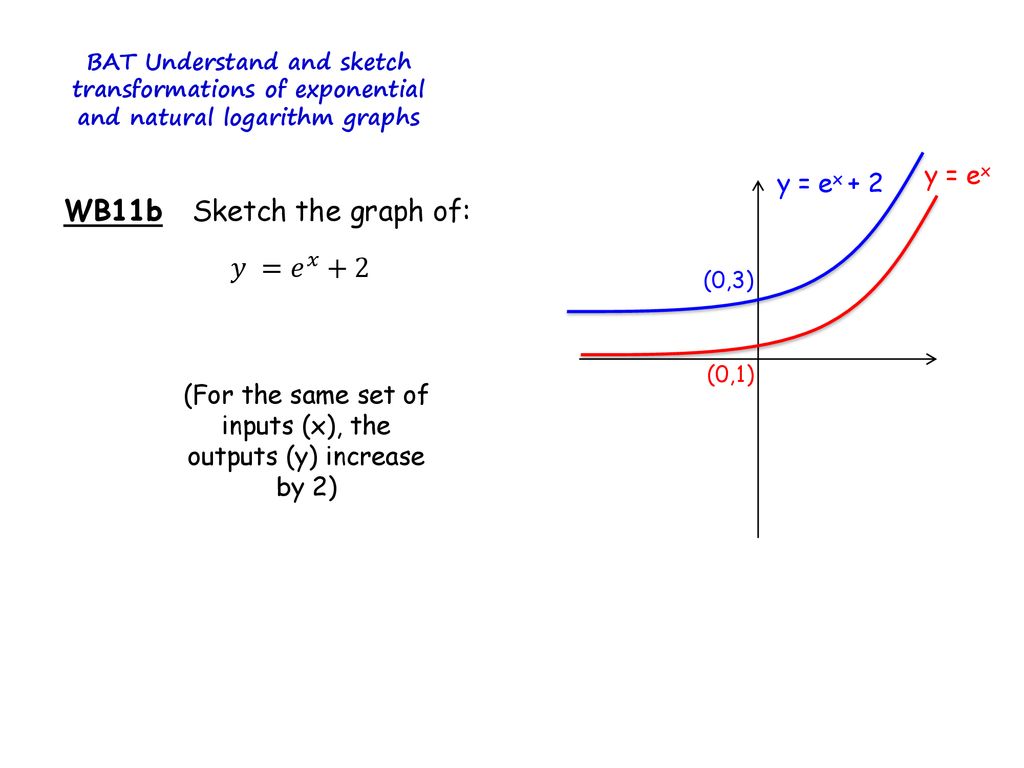
Exponential And Logarithms Transformations Graphs Ppt Download

Lesson 45
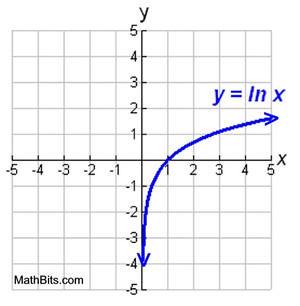
Natural Exponential Function And Natural Logarithmic Function Mathbitsnotebook Ccss Math
Graphing Exponential Functions



